Slips In Action
To demonstrate the capabilities of Slips, we will give it real life malware traffic and checking how Slips analyses it.

Saefko RAT
We provide the analysis of the network traffic of the RAT06-Saefko download here using Slips.
The capture contains different actions done by the RAT controller (e.g. upload a file, get GPS location, monitor files, etc.). For detailed analysis, check Kamila Babayeva’s blog Dissecting a RAT. Analysis of the Saefko RAT.
Disclaimer: The used Slips version in this demo is 1.0.2, alerts and evidence generated in this demo may be different than the alerts you may see using the latest version of Slips.
From the analysis we know that:
The controller IP address: 192.168.131.1 and 2001:718:2:903:f410:3340:d02b:b918
The victim’s IP address: 192.168.131.2 and 2001:718:2:903:b877:48ae:9531:fbfc
First we run slips using the following command:
./slips.py -e 1 -f RAT06_Saefko.pcap
First, Slips will start by updating all the remote TI feeds added in slips.conf
To make sure Slips is up to date with the most recent IoCs in all feeds, all feeds are loaded, parsed and updated periodically and automatically by Slips every 24 hours by our Update Manager, which requires no user interaction.
Afetr updating, slips modules start and print the PID of every successfully started module.

Then, we see the alert
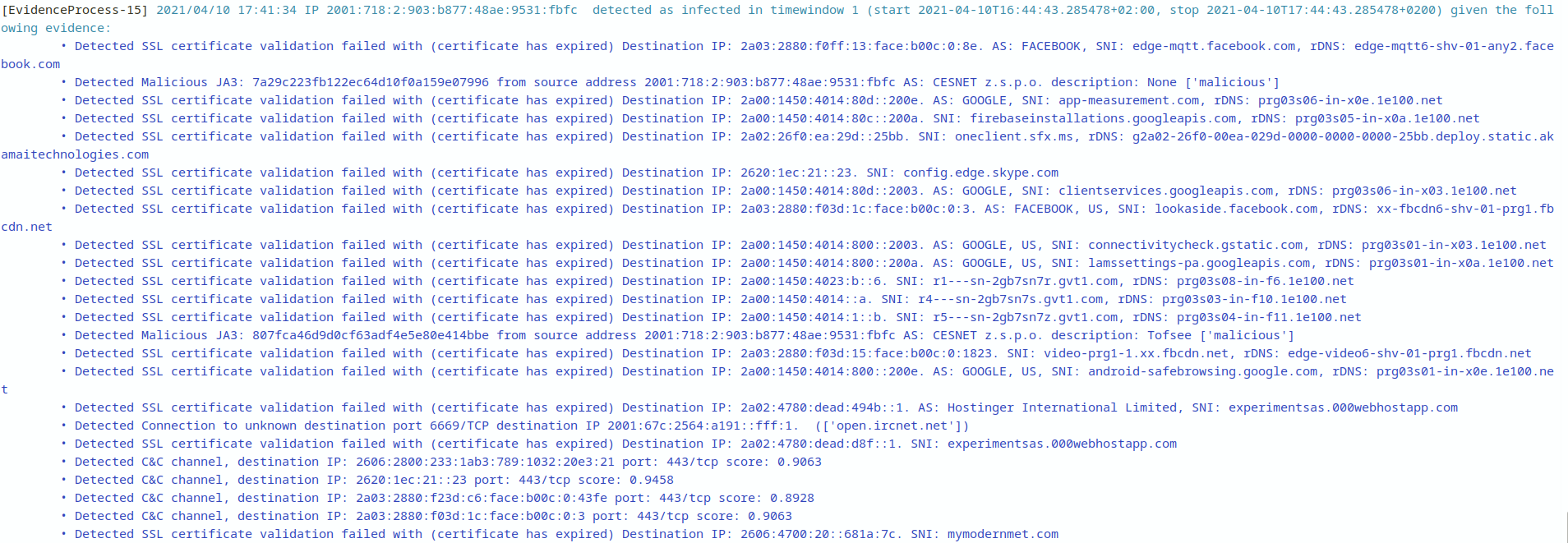
Alerts are printed by the evidence module, Slips detected IP 2001:718:2:903:b877:48ae:9531:fbfc as infected due to the above evidence See the difference between alerts and evidence here
Slips splits does detections in timewindows, each time window is 1 hour long by default and contains dozens of features computed for all connections that start in that time window.
So if an IP behaves maliciously at 4 PM, it will be marked as infected only during that hour, the next hour if no malicious behaviour occurs, slips will treat the traffic as normal.
This explains the start and stop timestamps in the alert start 2021-04-10T16:44:43.285478+02:00, stop 2021-04-10T17:44:43.285478+0200. This is the period (timewindow) in which this IP was behaving maliciously.
The difference between infected and normal timewindows is shown better in kalispo, our user interface.
You can start it in another terminal using ./kalipso.sh
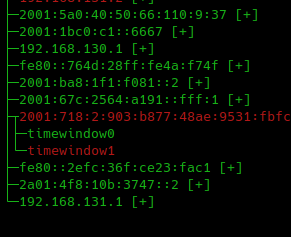
Figure 3
We can see that IP 2001:718:2:903:b877:48ae:9531:fbfc is infected only in timewindow1 as it’s marked in red and is behaving normally in timewindow0 as it’s colored in green.
We can see all the flows done by this IP in the infected timewindow in kalipso by pressing enter on timewindow1.
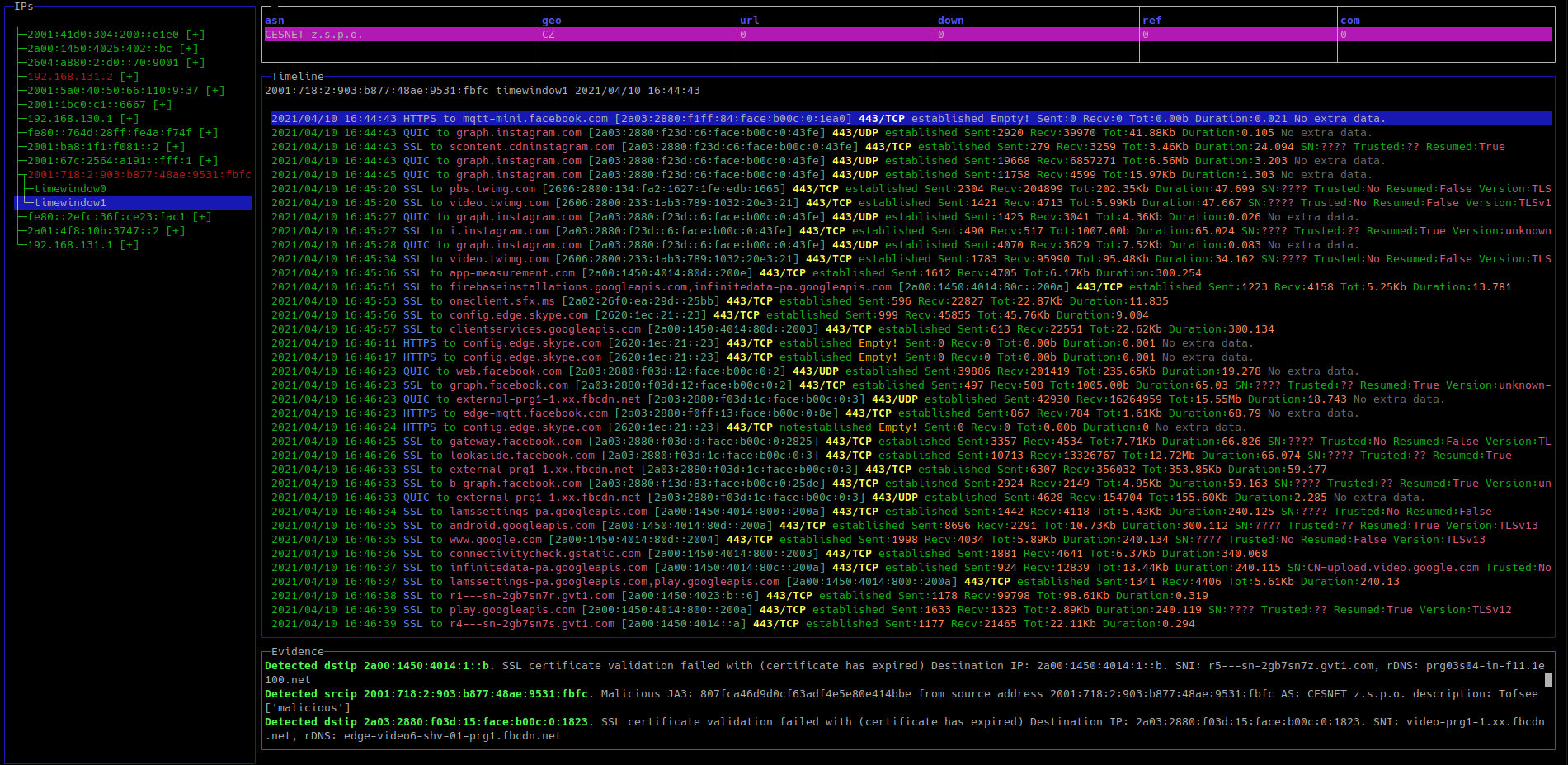
At the bottom box in kalipso we can scroll though the evidence and se what slips detected, this is the same evidence printed in Figure 3.
We can see the following detections in the evidence:
Detected Malicious JA3: 807fca46d9d0cf63adf4e5e80e414bbe from source address 2001:718:2:903:b877:48ae:9531:fbfc AS: CESNET z.s.p.o. description: Tofsee ['malicious']
JA3 fingerprint the client part of the SSL certificate. This indicates that the source IP 2001:718:2:903:b877:48ae:9531:fbfc was infected with one of the Tofsee malware family
Slips also detected the connection to the database:
SSL certificate validation failed with (certificate has expired) Destination IP: 2a02:4780:dead:d8f::1. SNI: experimentsas.000webhostapp.com
From the RAT analysis, we know that 000webhostapp.com is the web hosting service used by the C&C server.
Slips also detected
Connection to unknown destination port 6669/TCP destination IP 2001:67c:2564:a191::fff:1. (['open.ircnet.net'])
Connection to unknown destination port 8000/TCP destination IP 192.168.131.1.
From the APK list of IRC servers shown in the RAT analysis, we know that the phone connects on port 6669/TCP and 8000/TCP to different IRC servers to receive the malicious commands. The rDNS of the server is also printed in the alert open.ircnet.net
Our machine learning module rnn-cc-detection detected the C&C server using recurrent neural network
Detected C&C channel, destination IP: 192.168.131.1 port: 8000/tcp score: 0.9871
Slips also detected
Possible DGA or domain scanning. 192.168.131.2 failed to resolve 15 domains
The above detections are evidence that when accumulated, resulted in an alert.
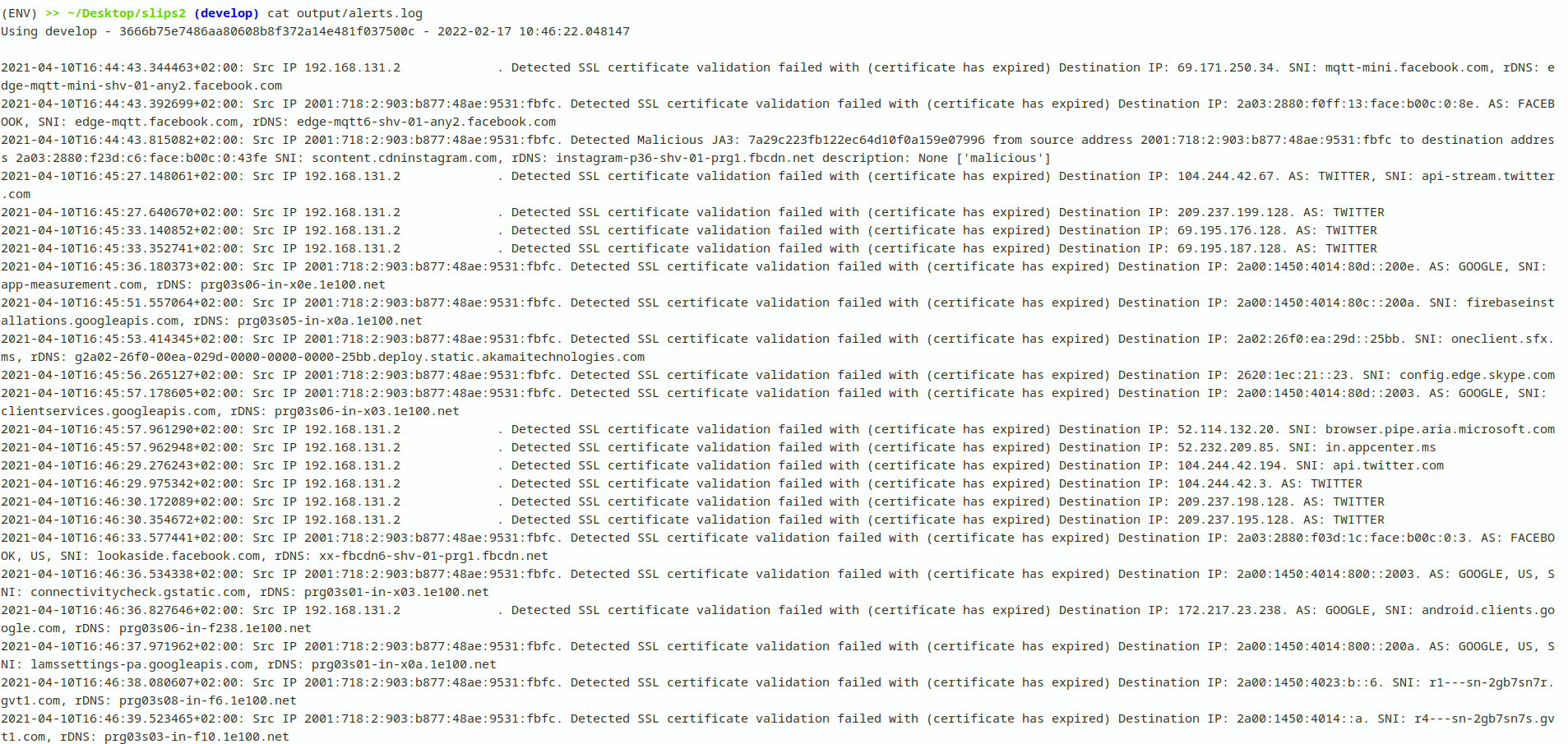
To view all evidence that slips detected including those that weren’t enough to generate an alert, you can
cat output/alerts.log
Slips also has another log file in JSON format so they can be easily parsed and exported. See the exporting section of the documentation.
The generated alerts in this file follow CESNET’s IDEA0 format.
cat output/alerts.json
Emotet
We will be analysing several Emotet PCAPs starting from infection, until Trickbot and Qakbot malwares are dropped.
The captures contain different actions done by the Emotet and trickbot controller. For detailed analysis, check Paloalto’s blog Examining Emotet Infection Traffic.
Emotet infection
We will be analysing this Emotet PCAP download here. password: infected
When running Slips on the PCAP
./slips.py -f Example-1-2021-01-06-Emotet-infection.pcap
We get the following alerts
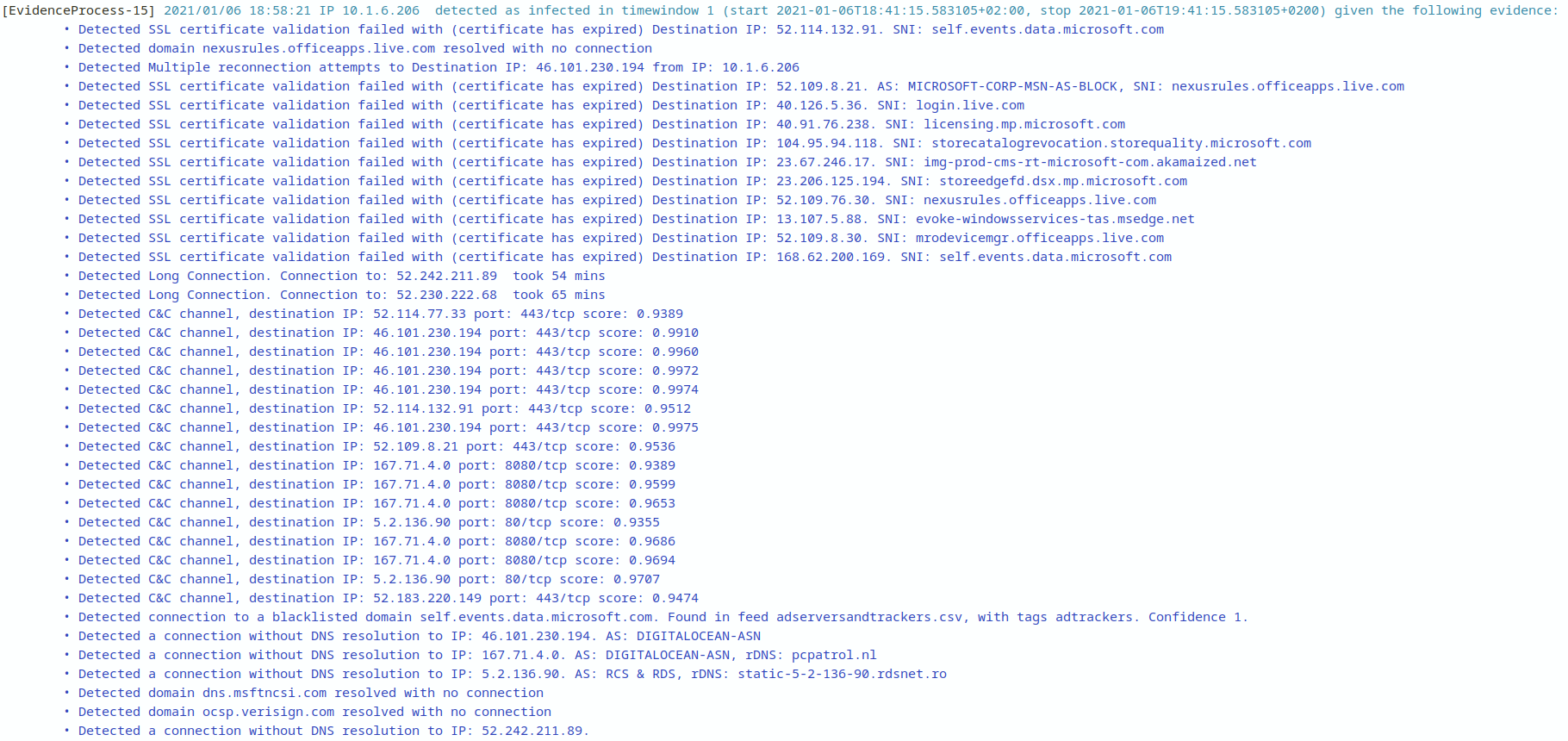
The reconnection attemps shown in the analysis
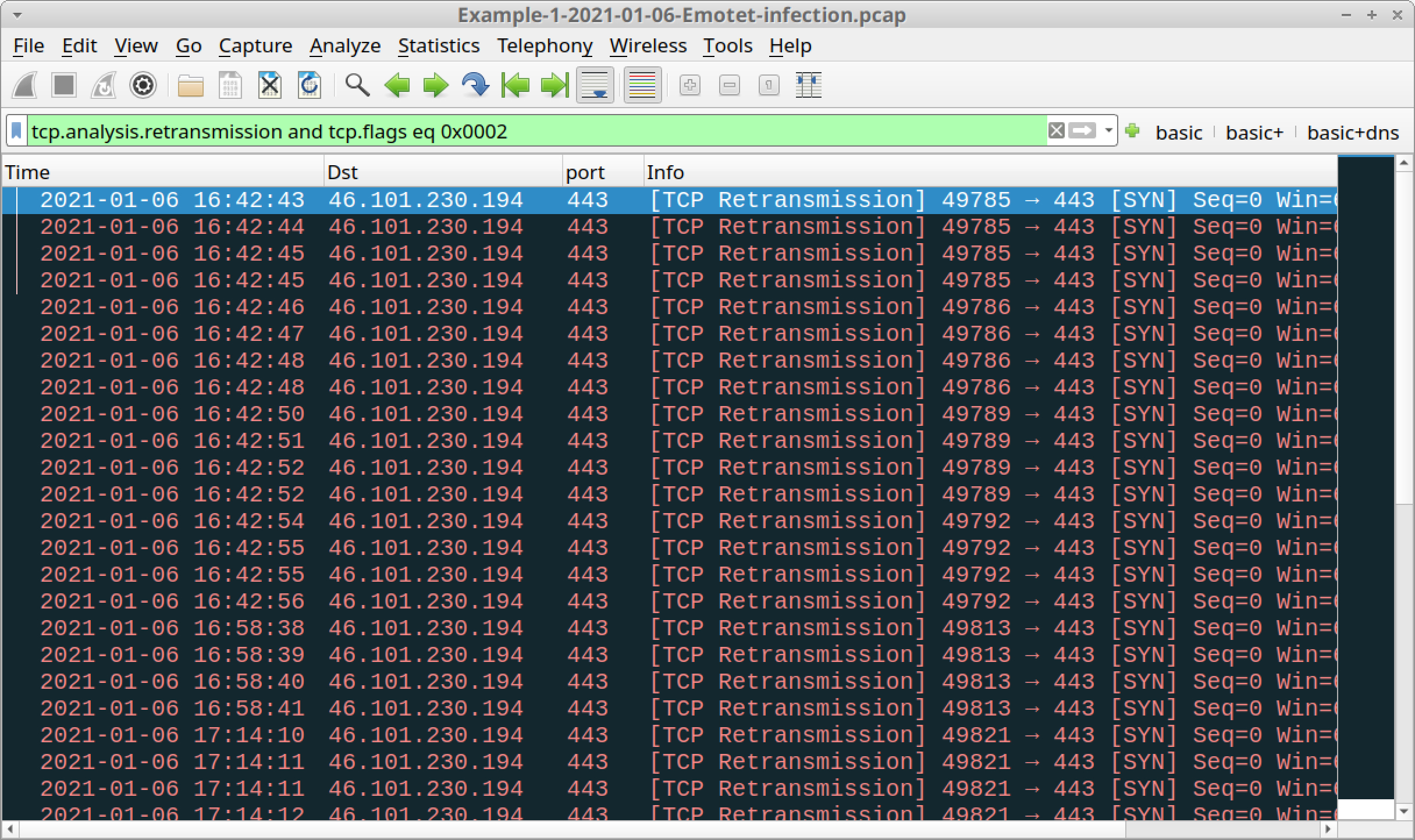
are detected by Slips in the following evidence
Detected a connection without DNS resolution to IP: 46.101.230.194
Detected Multiple reconnection attempts to Destination IP: 46.101.230.194 from IP: 10.1.6.206
Trickbot
Analyzing the next PCAP download here that contains the Trickbot traffic. password: infected
Running slips on the pcap
./slips.py -f Example-4-2021-01-05-Emotet-infection-with-Trickbot.pcap
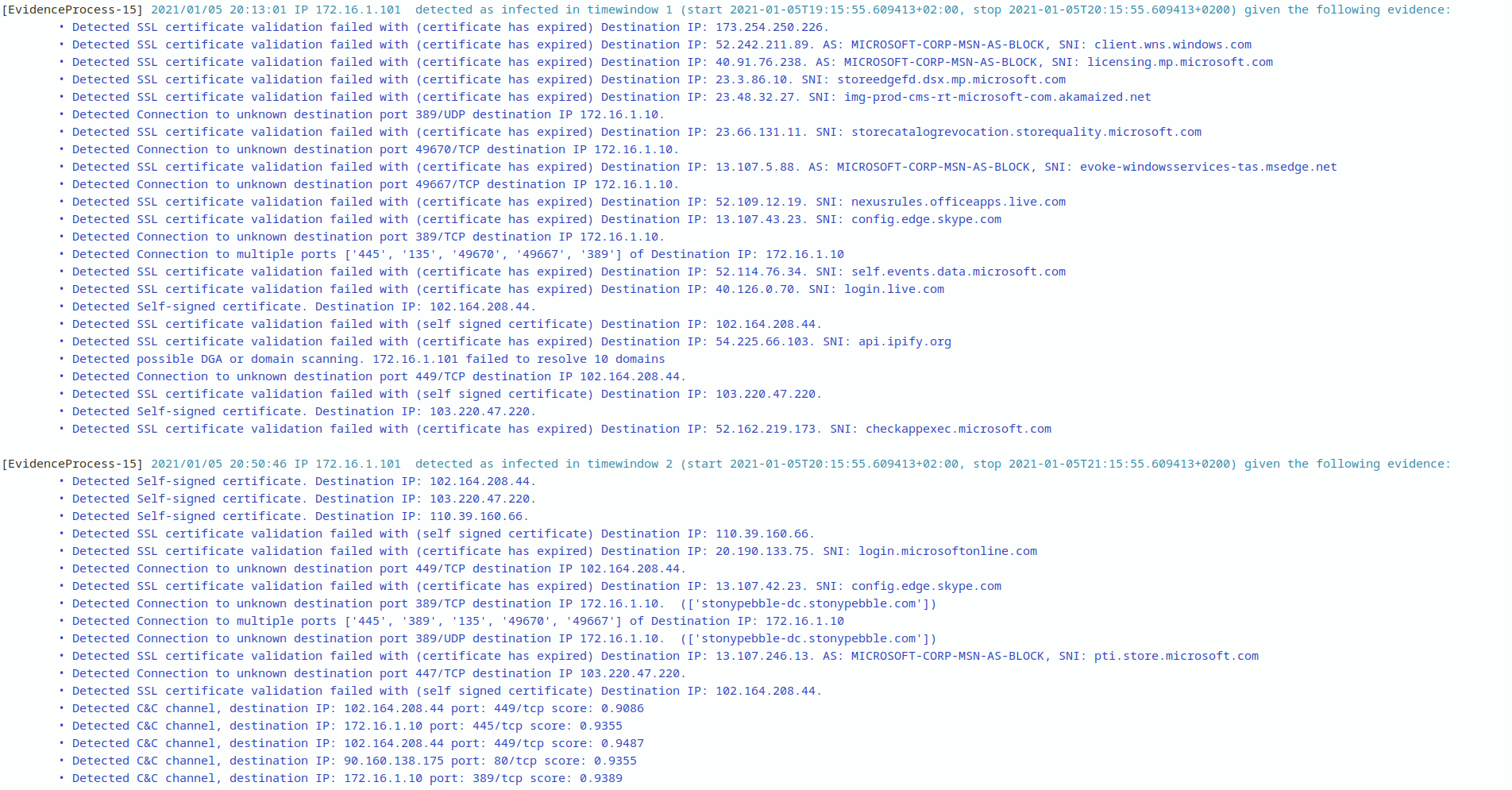
Slips detects a self signed SSL certificate to 102.164.208.44 which is the trickbot IP associated with data exfiltration
Detected SSL certificate validation failed with (self signed certificate) Destination IP: 102.164.208.44
Slips also detected
Detected a connection without DNS resolution to IP: 102.164.208.44.
and
Detected Connection to unknown destination port 449/TCP destination IP 102.164.208.44.
Qakbot
Analyzing the next PCAP download here that contains the Qakbot traffic. password: infected
Running slips on the pcap
./slips.py -f Example-5-2020-08-18-Emotet-infection-with-Qakbot.pcap

Slips detected that the victim 192.168.100.101 is infected with Qakbo using JA3
Detected Malicious JA3: 7dd50e112cd23734a310b90f6f44a7cd from source address 192.168.100.101 description: Quakbot ['malicious']
Detected Malicious JA3: 57f3642b4e37e28f5cbe3020c9331b4c from source address 192.168.100.101 description: Gozi ['malicious']
We can also see a Domain generation algorithm detection by the same victim 192.168.100.101
Detected possible DGA or domain scanning. 192.168.100.101 failed to resolve 40 domains
And an expired certificate to samaritantec.com. This domain was reported as hosting an Emotet binary on the same date.
Detected SSL certificate validation failed with (certificate has expired) Destination IP: 43.255.154.32. SNI: samaritantec.com
Slips then detected
Detected C&C channel, destination IP: 71.80.66.107 port: 443/tcp score: 0.9601
etected a connection without DNS resolution to IP: 71.80.66.107. AS: CHARTER-20115, rDNS: 071-080-066-107.res.spectrum.com
a quick search in virustotal shows that this IP 71.80.66.107 is associated with qakbot
and a port scan
Detected horizontal port scan to port 443/TCP. From 192.168.100.101 to 6 unique dst IPs. Tot pkts: 21. Threat Level: medium
DroidJack v4.4 RAT
Running Slips on DroidJack v4.4 RAT download here. password: infected.
The capture contains different actions done by the RAT controller(e.g. upload a file, get GPS location, monitor files, etc.). For detailed analysis, check Kamila Babayeva’s blog Analysis of DroidJack v4.4 RAT network traffic.
From the analysis we know that:
The controller IP address: 147.32.83.253
The victim’s IP address: 10.8.0.57
When running slips on the PCAP
./slips.py -f RAT02.pcap
We get the following alerts
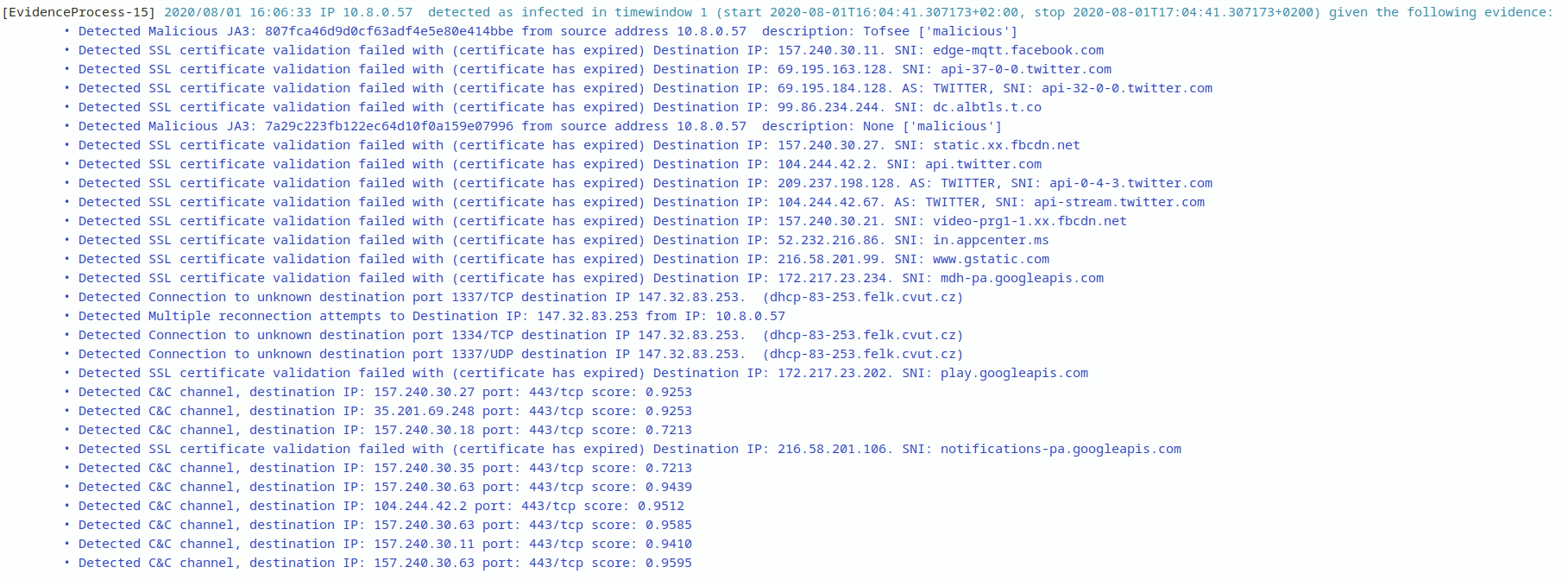
Slips detected the connection to the C&C server using an unknown port
Detected Connection to unknown destination port 1334/TCP destination IP 147.32.83.253.
Slips also detected the reconnection attemps made from the victim to the C&C server
Multiple reconnection attempts to Destination IP: 147.32.83.253 from IP: 10.8.0.57
Slips also detects connections without resolutions due to their wide usages among malware to either check internet connectivity or get commands fro the C&C servers.
Detected a connection without DNS resolution to IP: 147.32.83.253. AS: CESNET z.s.p.o., rDNS: dhcp-83-253.felk.cvut.cz
The indentification (AS, SNI, rDNS) of each IP, if available, is printed in every evidence generated by Slips.
Our Threat intelligence feed Abuse.ch detected a malicious JA3 indicating that the victim 10.8.0.57 is infected
Detected Malicious JA3: 7a29c223fb122ec64d10f0a159e07996 from source address 10.8.0.57 description: ['malicious']
And our machine learning models detected the C&C server
Detected C&C channel, destination IP: 147.32.83.253 port: 1334/tcp score: 0.9755
Slips creates a profile per each IP that appeared in the traffic. Each profile contains flows sent from this IP. Each flow is described with a specific letter which description can be found here.
Considering that, Slips detects the C&C channel over 1334/TCP. Slips’ machine learning module called LSTM detecting C&C channel is shown below

Slips did not detect periodic connection over 1337/UDP because the LSTM module focuses on TCP. But from the behavioral model of the connections over 1337/UDP shown below, we can conclude that the model is periodic and most of connections are of a small size.
